Emotional eating refers to the use of food as a coping mechanism to manage emotions rather than to satisfy physical hunger. It can occur in response to a variety of emotions, including stress, anxiety, boredom, or sadness. While emotional eating is a common behavior, it can lead to negative consequences, such as weight gain, poor body image, and difficulty managing emotions.
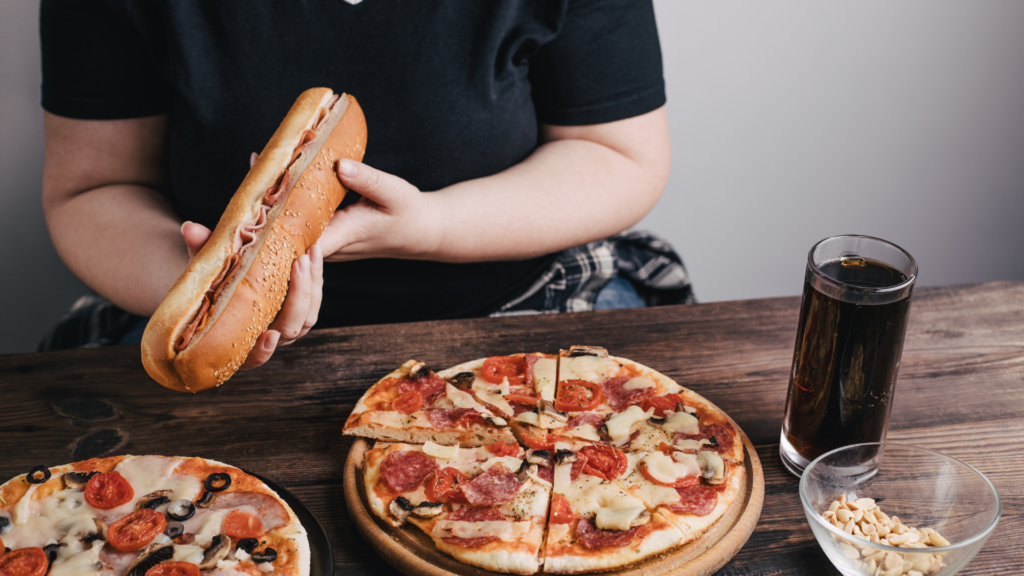

There are several different types of emotional eating, including:
- Boredom eating: This type of emotional eating occurs when people eat to fill a void or to pass the time, rather than because they are physically hungry.
- Stress eating: Stress eating is a common type of emotional eating that occurs when people turn to food as a way to cope with stress or anxiety.
- Comfort eating: Comfort eating refers to the use of food as a source of emotional support or comfort, often in response to difficult emotions or life events.
- Reward eating: Reward eating occurs when people use food as a reward or a way to celebrate, rather than as a response to physical hunger.
Emotional eating can also be a symptom of more serious eating disorders, such as:
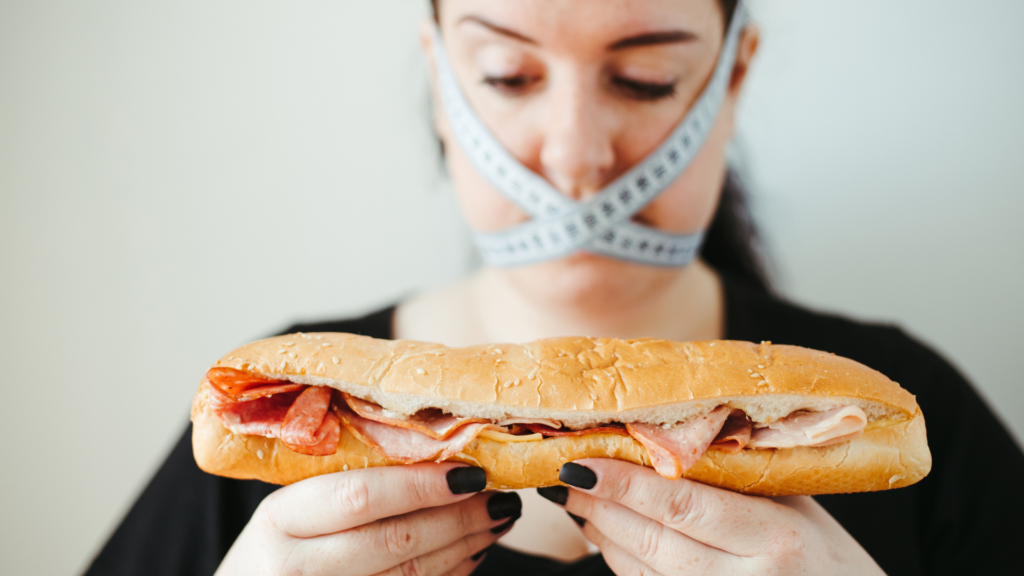

- Binge eating disorder: This disorder is characterized by frequent episodes of eating large amounts of food in a short period of time, often in secret, followed by feelings of shame or guilt.
- Anorexia nervosa: Anorexia is a severe eating disorder characterized by extreme weight loss and an obsessive fear of gaining weight. People with anorexia may restrict their food intake, exercise excessively, or engage in other unhealthy behaviors to control their weight.
- Bulimia nervosa: Bulimia is an eating disorder characterized by binge eating followed by compensatory behaviors, such as purging, fasting, or excessive exercise, to try to prevent weight gain.
If you are struggling with emotional eating or suspect that you may have an eating disorder, it’s important to seek help from a healthcare professional or mental health provider. With the right treatment and support, it is possible to overcome these challenges and develop healthy, balanced eating habits.
Emotional eating refers to the use of food as a coping mechanism to manage emotions rather than to satisfy physical hunger. It can occur in response to a variety of emotions, including stress, anxiety, boredom, or sadness. While emotional eating is a common behavior, it can lead to negative consequences, such as weight gain, poor body image, and difficulty managing emotions.
There are several different types of emotional eating, including:
- Boredom eating: This type of emotional eating occurs when people eat to fill a void or to pass the time, rather than because they are physically hungry.
- Stress eating: Stress eating is a common type of emotional eating that occurs when people turn to food as a way to cope with stress or anxiety.
- Comfort eating: Comfort eating refers to the use of food as a source of emotional support or comfort, often in response to difficult emotions or life events.
- Reward eating: Reward eating occurs when people use food as a reward or a way to celebrate, rather than as a response to physical hunger.
Emotional eating can also be a symptom of more serious eating disorders, such as:
- Binge eating disorder: This disorder is characterized by frequent episodes of eating large amounts of food in a short period of time, often in secret, followed by feelings of shame or guilt.
- Anorexia nervosa: Anorexia is a severe eating disorder characterized by extreme weight loss and an obsessive fear of gaining weight. People with anorexia may restrict their food intake, exercise excessively, or engage in other unhealthy behaviors to control their weight.
- Bulimia nervosa: Bulimia is an eating disorder characterized by binge eating followed by compensatory behaviors, such as purging, fasting, or excessive exercise, to try to prevent weight gain.
If you are struggling with emotional eating or suspect that you may have an eating disorder, it’s important to seek help from a healthcare professional or mental health provider. With the right treatment and support, it is possible to overcome these challenges and develop healthy, balanced eating habits.